Finding the forward and inverse kinematics of a robotic arm and using it to pick and place objects in a simulated environment.
Project Overview
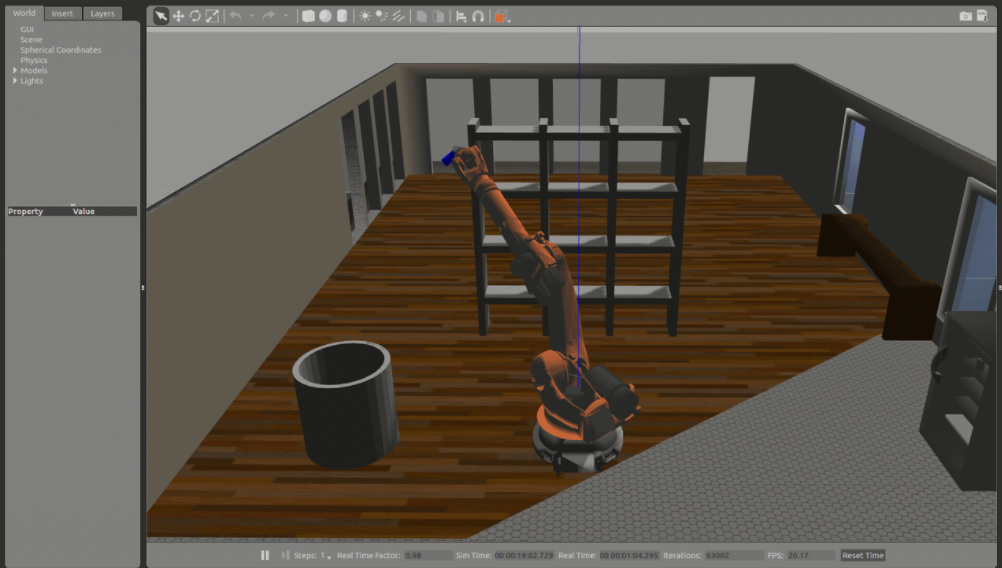
This project uses a Gazebo simulation platform to program a Kuka KR210 6 degree of freedom serial manipulator to pick up a cylinder from a shelf and drop it into a bin next to the manipulator.
The cylinder is located randomly on the shelf, Thus the robot needs to figure out his motor and joint angles and speeds to reach to the can from Global reference frames to his local frames. This could be achieved by calculating the inverse Kinematics of the Robot.
Contents
Kinematic Analysis
Kinematics is the a branch of mechanics that describes the motion of a system without considering the forces involved. Lots if the kinematics
After evaluating the the kr210.urdf.xacro, and comparing it with our DH parameter reference frames, we converted the Robot dimension information to the DH table as the following.
 ![alt text][image4]
Img:1 DH Parameter Reference Frames
![alt text][image4]
Img:1 DH Parameter Reference Frames
 ![alt text][image5]
Img:2 URDF file reference frames
![alt text][image5]
Img:2 URDF file reference frames
| Links | alpha(i-1)(rad) | a(i-1)(m) | d(i)(m) | theta(i)(rad) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0->1 | 0 | 0 | 0.33 + 0.42= 0.75 | q1 |
| 1->2 | - pi/2 | 0.35 | 0 | -pi/2 + q2 |
| 2->3 | 0 | 1.25 | 0 | q3 |
| 3->4 | - pi/2 | 0 | 0.96 + 0.54=1.5 | q4 |
| 4->5 | pi/2 | 0 | 0 | q5 |
| 5->6 | - pi/2 | 0 | 0 | q6 |
| 6->EE | 0 | 0 | 0.193 + 0.11 = 0.303 | 0 |
2. Using the DH parameter table you derived earlier, individual transformation matrices were created about each joint. In addition, also a generalized homogeneous transform between base_link and gripper_link was generated using only end-effector(gripper) pose
Python was used to create the individual transformation matrices about each joint, a snippet of the code is shown:
### Create symbols for joint variables to use in DH table
q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7 = symbols('q1:8')
d1, d2, d3, d4, d5, d6, d7 = symbols('d1:8')
a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6 = symbols('a0:7')
alpha0, alpha1, alpha2, alpha3, alpha4, alpha5, alpha6 = symbols('alpha0:7')
# Dictionary (associative array) DH Parameters table, q is theta
s = {alpha0: 0, a0: 0, d1: 0.75,
alpha1: -pi/2, a1: 0.35, d2: 0, q2: -pi/2+q2,
alpha2: 0, a2: 1.25, d3: 0,
alpha3: -pi/2, a3: -0.054, d4: 1.5,
alpha4: pi/2, a4: 0, d5: 0,
alpha5: -pi/2, a5: 0, d6: 0,
alpha6: 0, a6: 0, d7: 0.303, q7: 0,}
#### Homogeneous Transforms of neighbouring links
T0_1 = Matrix([[ cos(q1), -sin(q1), 0, a0],
[ sin(q1)*cos(alpha0), cos(q1)*cos(alpha0), -sin(alpha0), -sin(alpha0)*d1],
[ sin(q1)*sin(alpha0), cos(q1)*sin(alpha0), cos(alpha0), cos(alpha0)*d1],
[ 0, 0, 0, 1]])
T0_1 = T0_1.subs(s)
this gives the output:
T0_1=
⎡cos(q₁) -sin(q₁) 0 0 ⎤
⎢sin(q₁) cos(q₁) 0 0 ⎥
⎢ 0 0 1 0.75⎥
⎣ 0 0 0 1 ⎦
T1_2 =
⎡sin(q₂) cos(q₂) 0 0.35⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢ 0 0 1 0 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢cos(q₂) -sin(q₂) 0 0 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣ 0 0 0 1 ⎦
T2_3 =
⎡cos(q₃) -sin(q₃) 0 1.25⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢sin(q₃) cos(q₃) 0 0 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢ 0 0 1 0 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣ 0 0 0 1 ⎦
T3_4 =
⎡cos(q₄) -sin(q₄) 0 -0.054⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢ 0 0 1 1.5 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢-sin(q₄) -cos(q₄) 0 0 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣ 0 0 0 1 ⎦
T4_5 =
⎡cos(q₅) -sin(q₅) 0 0⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢ 0 0 -1 0⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢sin(q₅) cos(q₅) 0 0⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣ 0 0 0 1⎦
T5_6 =
⎡cos(q₆) -sin(q₆) 0 0⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢ 0 0 1 0⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢-sin(q₆) -cos(q₆) 0 0⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣ 0 0 0 1⎦
###Notice becurse of the Gripper's reference frame has the same orientation as joint6
(the one before it) the transformation matrix in the rotation part is the identity matrix.
T6_G =
⎡1 0 0 0 ⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢0 1 0 0 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢0 0 1 0.303⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣0 0 0 1 ⎦
##From-Base Link to End-Effector Transformation Matrix To Determine the complete homogeneous transform between the base link and the gripper link (end-effector) using just the end-effector pose (position ==(Px,Py,Pz)==+rotation ==(Roll-Pitch-Yaw== angles of the end-effector)).
T BL_EE =
⎡ Px ⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢ RT Py ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢ Pz ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣0 0 0 1 ⎦
Where RT (Rotation transform) can be the result of the intrinsic rotations of the end gripper around the given roll, pitch, yaw angles=Rx(rol)*Ry(yaw)*Rz(pitch).
Note: this gives the same result of ` T6_G` after substituting the Theta angles the Kuka210
T BL_EE =
⎡ Px ⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢ RT Py ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢ Pz ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣0 0 0 1 ⎦
Substituting the Thetas with Zeros gives the cumulative distance of the robot from Base Link to End Effector:
T_EE=
[[ 1.0, 0, 0, 2.153],
[ 0, 1.0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 1.0, 1.946],
[ 0, 0, 0, 1]]
##Inverse Kinematics
Inverse Kinematics is computing the joint angles when knowing the end effector’s position and orientation. Therefore, when knowing the target location, IK computes the amount of movement and direction that needs to be executes to reach that location, making it an important chapter in Robotics.
Because the Kuka KR210 joints (4 5 and 6) satisfies that its:
Three neighboring joint axes intersect at a single point
The inverse Kinematic problem it is solvable in closed-form with wrist center at joint 5.
which is able to rotate the end effector to the exact orientation required for the task at hand. The first three joints move the wrist center to a position where it has enough mobility to orient itself to the angle required.
